DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT)(
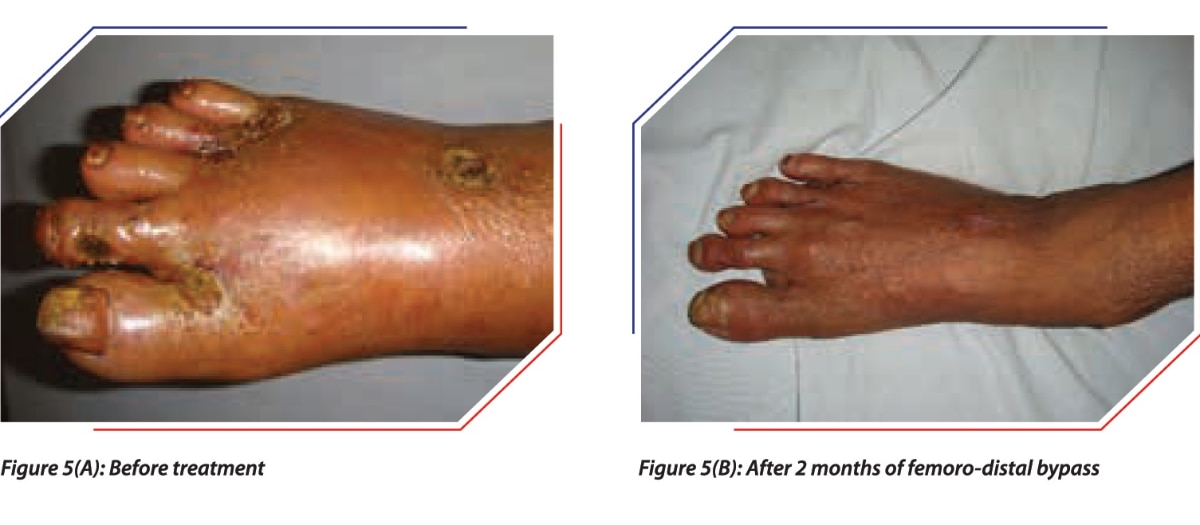
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, usually in the legs. Deep vein thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling. Sometimes there are no noticeable symptoms.Blood clot in leg veinA blood clot in a leg vein may cause pain, warmth and tenderness in the affected area.You can get deep vein thrombosis (DVT) if you have certain medical conditions that affect how the blood clots. A blood clot in the legs can also develop if you don't move for a long time. For example, you might not move a lot when traveling a long distance or when you're on bed rest due to surgery, an illness or an accident.Deep vein thrombosis can be serious because blood clots in the veins can break loose. The clots can then travel through the bloodstream and get stuck in the lungs, blocking blood flow (pulmonary embolism). When DVT and pulmonary embolism occur together, it's called venous thromboembolism (VTE).Products & ServicesAssortment of Compression Products at Mayo Clinic StoreBook: Mayo Clinic Family Health Book, 5th EditionNewsletter: Mayo Clinic Health Letter — Digital EditionSymptomsDeep vein thrombosis (DVT) symptoms can include:Leg swellingLeg pain, cramping or soreness that often starts in the calfChange in skin color on the leg — such as red or purple, depending on the color of your skinA feeling of warmth on the affected legDeep vein thrombosis can occur without noticeable symptoms.When to see a doctorIf you develop symptoms of DVT, contact your health care provider.
READ MORE

 +918048030553
+918048030553